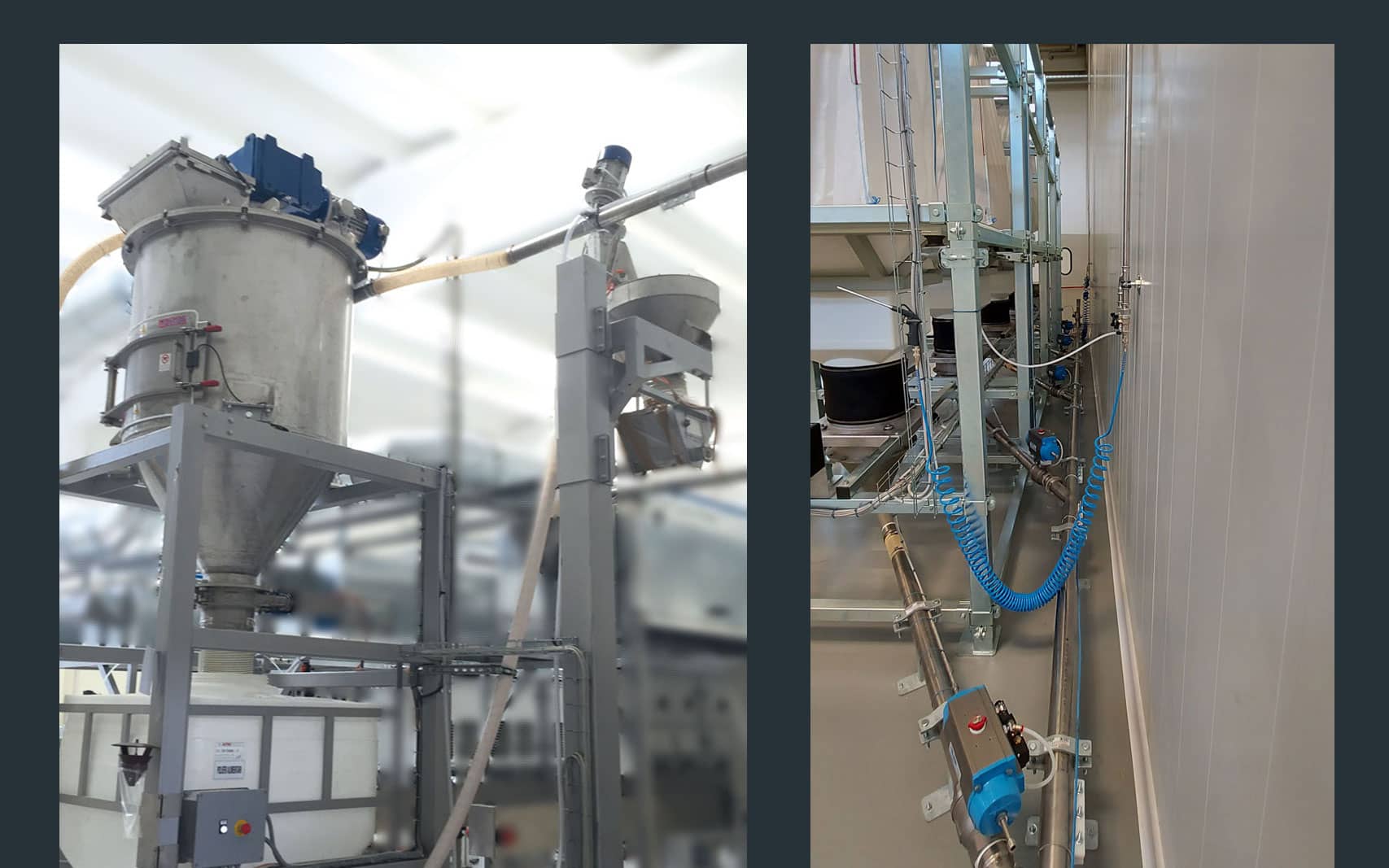

pneumatic conveyor
Vacuum conveying enables hygienic transfer of materials, even on long and twisting routes

Vacuum conveying enables hygienic transfer of materials, even on long and twisting routes
We design and manufacture custom pneumatic systems in dense phase and dilute phase to meet the needs and requirements of the food, chemical, and plastic industries.
GIMAT has implemented dilute phase pneumatic conveying systems both vacuum and positive pressure.
They are used when is necessary to charge and weight content into powder mixers with multiple components, starting from different big bags or fully emptying previosly batched hoppers.
It is an easy to install system, particulary suitable to convey food and potential explosive powders in a safe and clean way for long distances.
Gimat powder mixers have been studied to be put under vacuum and filled up pneumatically, realizing a high speed and economical filling system, very easy to clean.

ATEX - Explosion Proof Protected
On request Gimat pneumatic conveying equipment can be designed and manufactured in compliance with the Directive ATEX 2014/34/EU FOR ZONE 2-22 / ZONE 1-21
Electric vacuum or pneumatic pumps
Easy removable filter groups, for fast cleaning
Direct suction into the vertical ribbon mixer
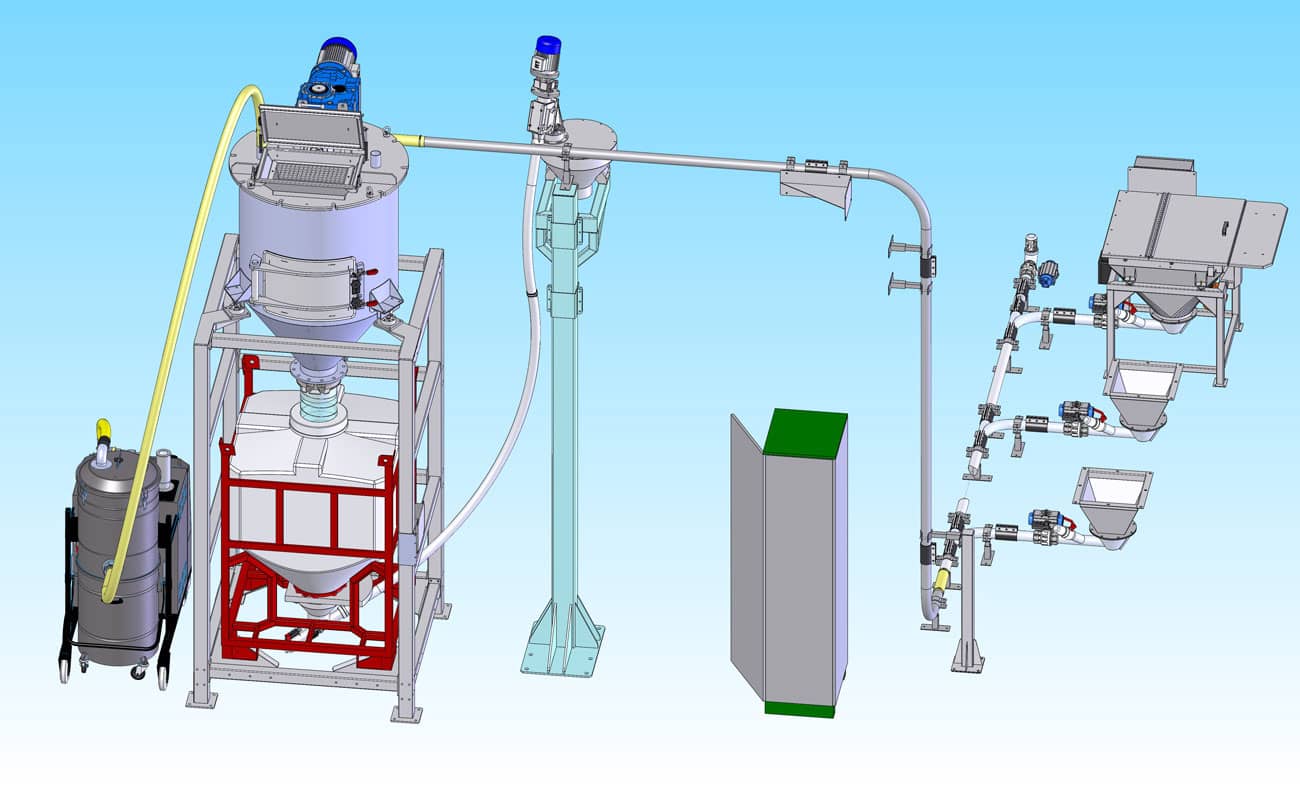
Here an example of a typical pneumatic system designed by Gimat. A pneumatic conveyor system in the dilute phase empties the big bags. A cyclone separator is integrated in the vertical ribbon mixer. The content of the mixer is then transferred into a container holding the same blend of materials. To prevent the separation of the previously obtained product mix, a flexible screw conveyor is used to transport the blend.
In lean phase pneumatic conveying, the material to be transported is suspended in the airstream and the ratio of material to air is low, meaning that the material is conveyed in a dilute phase. Lean phase pneumatic conveying systems can be further categorized into two main types based on their operating principle: pressure conveying and vacuum conveying.
In pressure conveying systems, the material is moved through the conveying line by air or gas pressure supplied by a blower or compressor. The material is fed into the inlet point with a rotary valve that dose the product into the air flow ensuring a correct and constant product/air ratio. Once in the flow is carried along the conveying line to a receiving vessel at the discharge point, where it is separated from the air stream.
Vacuum conveying systems, on the other hand, use a vacuum to draw materials through the conveying line. The vacuum is created by a vacuum pump or blower at the destination point. Material is sucked into the system from feed points and transported to the destination, where it is separated from the air stream.
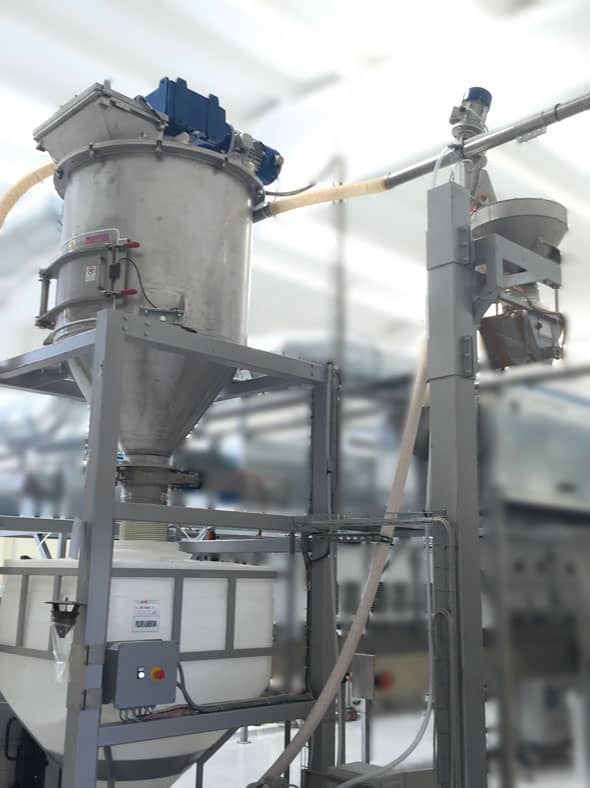

The main factors we need to analyse to design a pneumatic conveying system for you are:
The variety of cases we have dealt with over the past 50 years allows us to say that no two projects are the same, and the choice of one system over another depends precisely on the combination of many factors. Here, we summarise the general characteristics of both systems. Our R&D department has capitalised on the experience gained over the years to make the most of the advantages of both methods.
Dense phase: pros and cons
Dilute phase: pros and cons